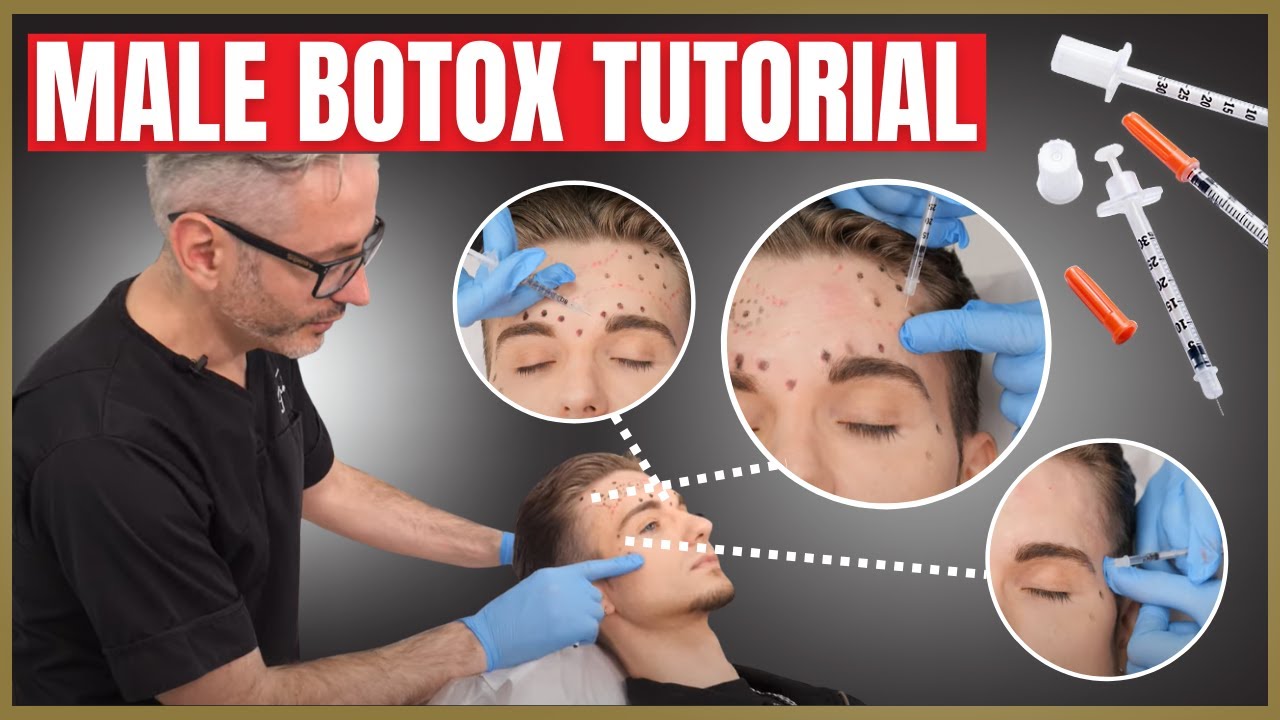
Effective Injection Techniques for Male Facial Treatment
This week I’d like to share with you a simple treatment on a male. Men are different to inject than females, obviously, and it’s all about the eyebrows. So, I hope you can learn a lot from this very simple, basic treatment that we all need to know when you start treating men.
Understanding the Seven Point Injection Strategy
This is a seven point injection strategy designed to minimize movement. It is acceptable to use a five point or even a three point strategy if you don’t mind a little bit of lateral movement. The downside of this technique is a lateral pull, which some patients do not like. Discuss it with your patient and choose the best plan for them.
Importance of Precision
Remember, the lateral injections are most likely to affect the frontalis and cause eyebrow heaviness, so you must be precise here. Treating the frontalis is the trickiest muscle. In masculine faces, the frontalis muscle often goes higher up and it’s stronger, more securely into the hairline. This becomes a problem if you treat with a feminine pattern, you will get additional movement high up near the hairline and follow-ups will occur.
Marking Healthy Areas
From a safety perspective, the first thing to do is mark healthy areas where you do not want to inject. Here I’m marking out the inferior margin of where I will inject, leaving a two centimeter margin approximate from the eyebrows. It’s also helpful to consider where the lines and wrinkles are here. I’m also marking out where I see the aponeurosis where there’s minimal movement. And this is simply to save on botulinum toxin. If you were to inject in this area it would not cause a side effect, it’s just a waste of money.
Spacing Out Injections
What you’re left with then is a smaller area to focus your attention on to decide where to inject. We now need to consider how far does botulinum toxin diffuse from an injection point. The rule of thumb is about 1.5 centimeters. This enables me to space out my injections. It’s effectively a marble size area of diffusion, and the goal now is to fill this frontalis area with marble size injection points.
Choosing Injection Points
To make it easier to space them out, choose your first medial injection point and then your most lateral injection point, bearing in mind the spread of the toxin. It then makes it easier and clearer to decide where to put your injections between those points. That’s what it looks like when done more efficiently with practice. If in doubt, place one more securely as it’s a very safe place to treat.
Handling Post-Procedure Lines
Men who get lines and wrinkles higher up after a procedure will often refer to them as horns. And this is why we need to treat well on the first pass. This is true, even if the muscle is not that strong as it tends to increase in activity after a procedure where it has not been treated. Though there are always exceptions, a masculine frontalis tends to be stronger, more superior, and laterally and up into the hairline than a female.
Assessing the Orbicularis Oculi Muscle
When assessing the orbicularis oculi muscle I tend to start by looking for the thickest part of the muscle which tends to follow the trajectory of the eyebrow. You can see that the orbicularis oculi is also an accessory muscle for cheek elevation. This is not something that I want to completely neutralize.
Maintaining Natural Expression
I don’t want to completely neutralize the orbicularis oculi or his face will look heavy or sad even, when he’s not smiling, getting rid of the wrinkles at the expense of causing another problem. Typically, this tends to look drawn. That’s the reason I make the small adjustment here. And I will use lower doses lower down.
Injecting the Glabella Complex
The goal here is to reduce the risk of botulinum toxin making its way into the orbit affecting the levator palpebrae muscle and secondly, to avoid treating the frontalis, which overlaps with the corrugator. The way I avoid this is by being at the right depth. Compression during injection is one simple way of reducing the risk. You can see my finger here inferior to the eyebrow compressing on the superior aspect of the orbit. I’m also angling my needle so that it’s pointing away from the orbit. In my mind’s eye I’m aiming for a D point underneath the mark I’ve placed on the forehead. I’m not penetrating through the mark left by the pencil.
Depth of Injections
Corrugator is deep medially, intermediate, at the intermediate injection point and superficial laterally. My injections are deep medially, in this case, four units, although I would commonly use six units in a man if I knew they required more. The muscle is less deep here, as it is traversing laterally it becomes more superficial, so I am now at intermediate depth. For the final injection I’m most lateral. I’m medial to the insertion point and injecting one to two units. The procerus is the easiest and safest injection.
Repeating the Process
Then, repeat the process on the other side of the face. We’re aiming for the same depth in the skin, staying medial to the mid pupillary line may decrease the chance of affecting the frontalis, which is a vulnerable spot for causing eyebrow asymmetry or eyebrow ptosis. Treating the forehead, though technically the hardest area to plan, it’s the simplest area to inject. We only have the frontalis muscle nearby. We have skin, hypodermis, fascia muscle that we want to inject, loose area tissue and the bone. The botulinum toxin injections are effective in all the layers, though probably more effective directly into the muscle or underneath the muscle.
Injection Depth Estimation
I aim for injecting into the muscle as I do not like pushing on the bone with a needle I’m going to use for subsequent injections. And injecting into the dermis is also more painful and less effective. I’m estimating the depth of the muscle here with experience. We have three skin hypodermis, then into the muscle. As the injections are technically easy, it’s a relatively quick process. For a man wanting a relatively natural treatment to get it across in all these areas is sufficient in most people, although licenses now include much higher doses of four units per injection point.
Treating the Orbicularis Oculi
Now treating the orbicularis oculi, the key here to avoid side effects and risks is to stay superficial. The skin is very thin. We only need to go one to two millimeters beneath. We’ll be approximately through the fat and resting just above the orbicularis oculi muscle. So how superficial it is, many new injectors like to inject all the way in and this is why side effects, even simple ones like bruising, are more common than they need to be.
Maintaining Accuracy
It’s particularly important to use accuracy in the inferior part where the risk of zygomaticus major being affected is highest.
Read More: Non-Surgical Face Lift Options: A Guide to Facial Rejuvenation